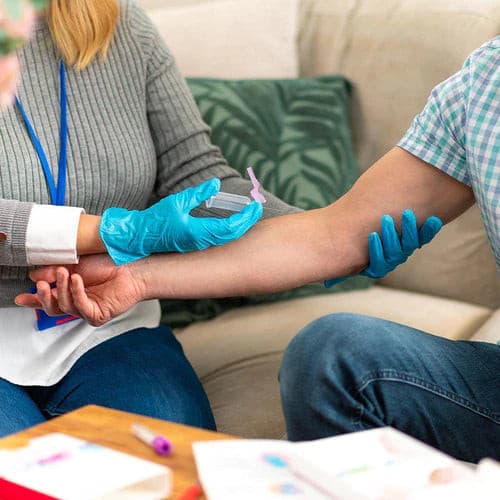
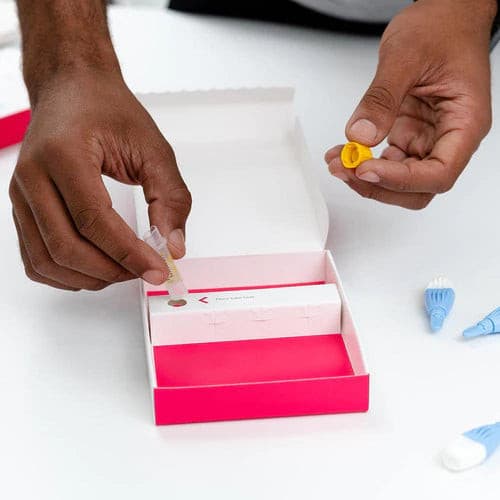
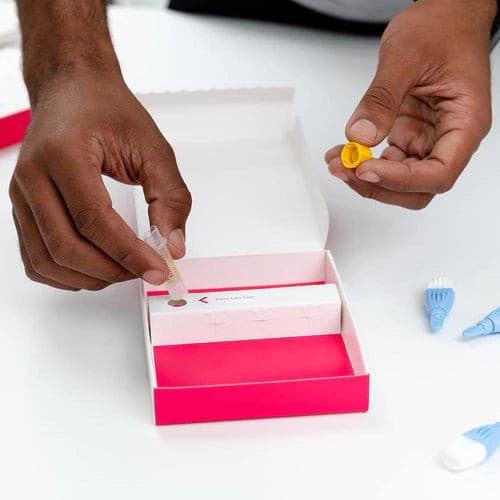
About Description
- Indicate the vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B12, C, D, E
- measure the beta carotene and red cell folate
Why People Choose Us

Quick & Easy
No appointment or long waiting times
Discreet Packaging
Plain packaging with no medical stamps or marks

Confidential Service
Your information stays with us and private payment

UK Medication
Dispensed by registered UK pharmacists
Vitamins (11 Biomarkers)
Your body requires vitamins as necessary nutrients to function properly. They must come from the food you consume because you cannot manufacture them yourself. There are two categories of vitamins: fat-soluble and water-soluble.
Oily foods, whether animal- or plant-based, contain fat-soluble vitamins like vitamins A, D, E, and K.
You don't need to eat them every day because your body stores them in fatty tissue and the liver. You must consume meals containing these nutrients more regularly because the majority of water-based vitamins, such as vitamin C, are not stored in the body.
A balanced diet should provide you with all the vitamins you require. But occasionally, dietary decisions or medical issues might make us vitamin deficient.
Vitamin E- Alpha Tocopherol
Antioxidants like vitamin E are crucial in defending against the harm done to bodily tissue by unstable chemicals called free radicals, which are created by cigarette smoke, sunshine, pollution, and chemical processes within the body.
In addition to helping the body absorb vitamin K and maintaining a healthy immune system, vitamin E is crucial for the production of red blood cells.
Vitamin C
Numerous fruits and vegetables, such as oranges, peppers, strawberries, blackcurrants, tomatoes, and potatoes, contain the water-soluble vitamin C.
Vitamin C is essential for collagen formation, iron absorption, wound healing, strong bones and teeth, and tissue growth and repair.
It also functions as an antioxidant and fends off dangerous free radicals.
Vitamin A
Retinol, a fat-soluble vitamin called vitamin A, is present in animal products such eggs, dairy, liver, and kidneys.
It is crucial for healthy cell division (cellular differentiation), clear vision, and the proper growth of an embryo and foetus.
Vitamin B6
The B vitamins are a family of eight water-soluble vitamins that are essential for red blood cell production, healthy central nervous system function, and cellular metabolism.
Vitamin B2
The B vitamins are a family of eight water-soluble vitamins that are essential for the creation of red blood cells, the correct function of the central nervous system, and the metabolism of cells.
Vitamin B1
The B vitamins are a family of eight water-soluble vitamins that are essential for red blood cell production, healthy central nervous system function, and cellular metabolism. All of the body's cells require adenosine triphosphate, which is created by the water-soluble vitamin thiamine (B1).
Beta-Carotene
Carrots are orange because of beta-carotene, a fat-soluble pigment present in plants. Beta-carotene is converted by your body into vitamin A (retinol), and because your body only converts what it needs, this is a safe supply of vitamin A.
Vitamin A in excess can be hazardous. Vitamin A is necessary for healthy vision, cellular differentiation, normal cell reproduction, and the development of an embryo and foetus. As an antioxidant, beta-carotene shields the body from harmful free radicals. Carrots, tomatoes, spinach, lettuce, sweet potatoes, squash, and broccoli are foods that contain beta-carotene.
Folate -Red Cell
A coenzyme in the metabolism of amino acids is folate, a B vitamin. Additionally, it is necessary for the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines, which are necessary for the production of red blood cells and DNA.
Make sure your folate levels are normal if you're thinking about getting pregnant because folate is also crucial during the first trimester of pregnancy. Red Cell Folate is a marker of the body's folate reserves.
Vitamin D
Together with calcium, vitamin D is essential for bone maintenance. It is crucial for both protein synthesis and muscle function.
Other non-musculoskeletal advantages, such as immunological regulation, defence against chronic diseases, and improved sports performance, have also been emphasised by more recent study.
Maintaining adequate amounts of vitamin D is crucial for athletes. When your skin is exposed to sunshine, it can produce vitamin D.
This is challenging in the UK, especially during the winter. Even if they exercise outside, people in the UK frequently have low vitamin D levels.
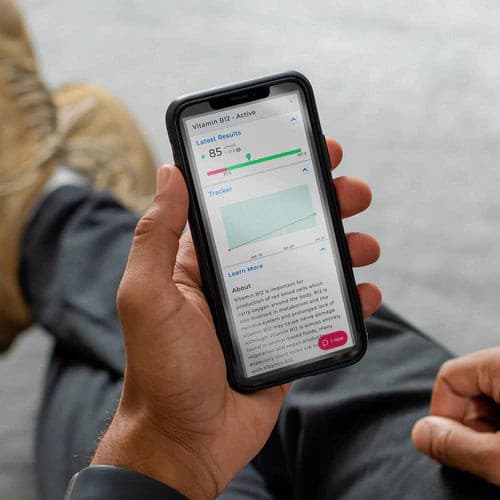
Vitamin B12 - Active
The generation of red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body, depends on vitamin B12.
Additionally essential for metabolism and the nervous system, vitamin B12 deficiency can harm nerves over time.
Although plant milks are increasingly frequently enriched with vitamin B12, vitamin B12 is still nearly exclusively found in meals derived from animals.
Vitamin B3
The B vitamins are a family of eight water-soluble vitamins that are essential for red blood cell production, healthy central nervous system function, and cellular metabolism.
Red Blood Cells (2 Biomarkers)
The most prevalent form of blood cell, the red blood cell, is responsible for transporting oxygen to your tissues through your circulatory system.
Your bone marrow continuously produces red blood cells to replace those that are lost as a result of bleeding or cell ageing. Your red cell count should remain consistent, but some health issues can result in abnormally few or excessively numerous red cells, abnormally fast cell death, or abnormally shaped red cells.
The amount of oxygen given to your tissues is affected if you are not creating enough red blood cells, which causes anaemia and its accompanying symptoms of weariness and pale skin. Headaches, blurred vision, and an enlarged spleen can all be symptoms of excessive red blood cell production.
Haematocrit
The haematocrit (HCT) scale measures how much space (volume) red blood cells occupy inside the blood.
MCHC
The average amount of haemoglobin in your red blood cells is called the MCHC (mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration).
Red blood cells use the chemical haemoglobin to carry oxygen throughout the body.
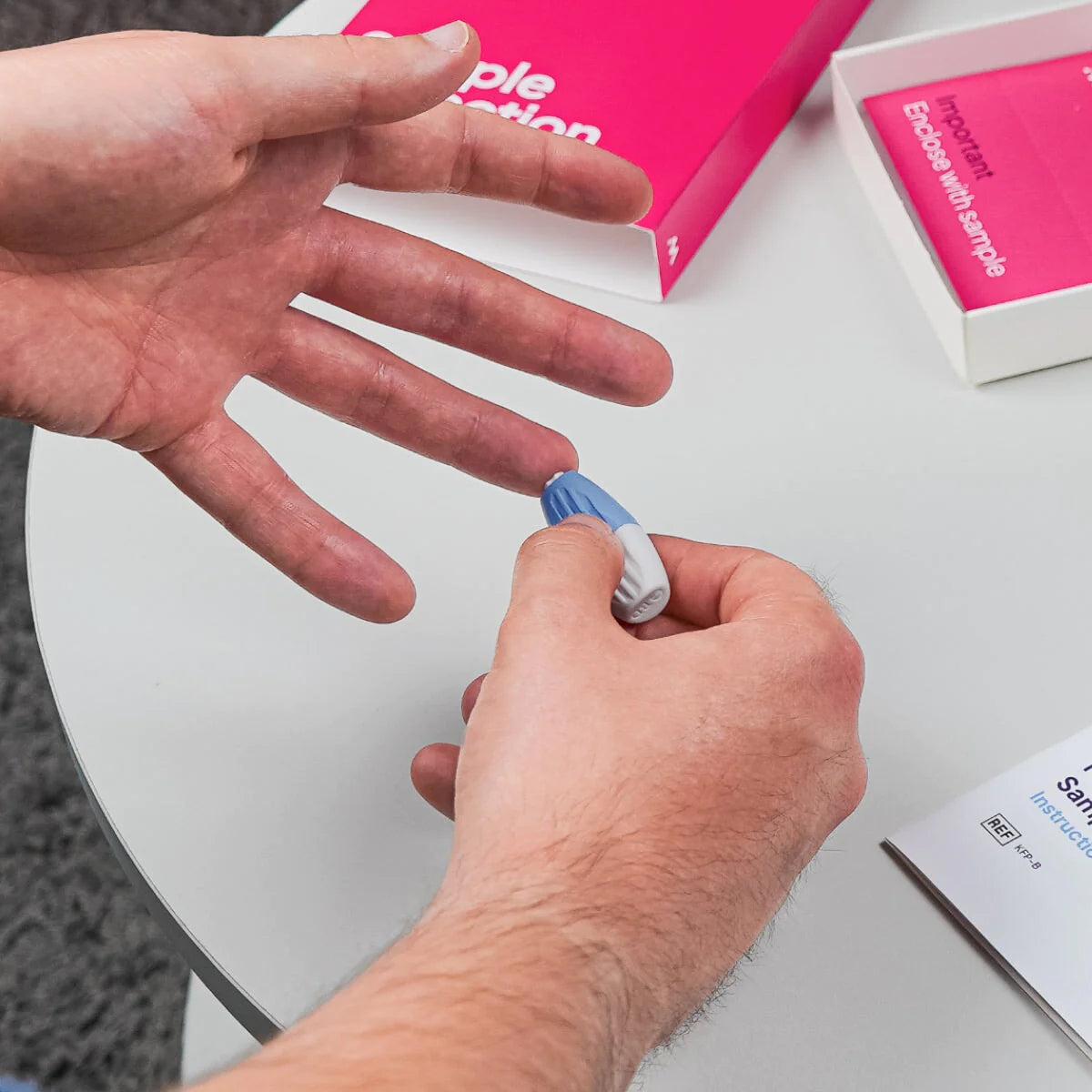
Easy Steps for your Medicine

Complete a consultation.
With complete privacy and confidentiality your form is checked by a pharmacist independent prescriber.
Choose your treatment.
From the list approved by the prescriber, choose your preferred treatment and then wait for it to be dispensed by UK Meds online pharmacy.
Receive your delivery
With next day delivery options available, you can have your treatment sent out to you discreetly within hours.Our Happy Customers
Rated Us for our Service Excellence
 Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists
Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists

 How it works
How it works Help
Help Account
Account
 Basket
Basket