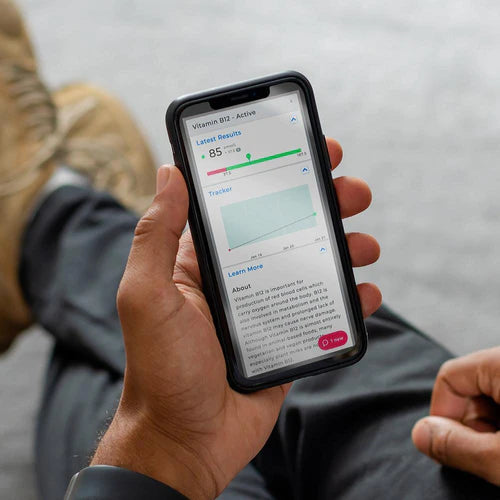
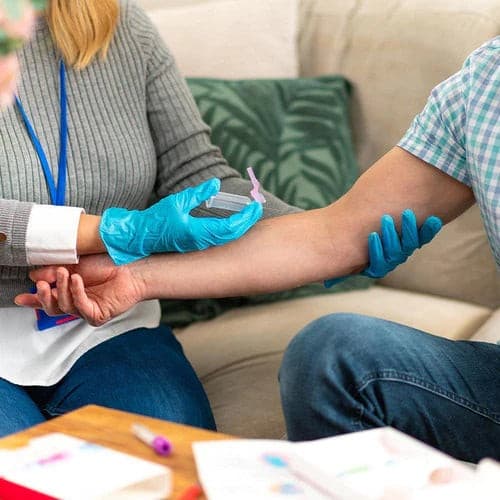
About Description
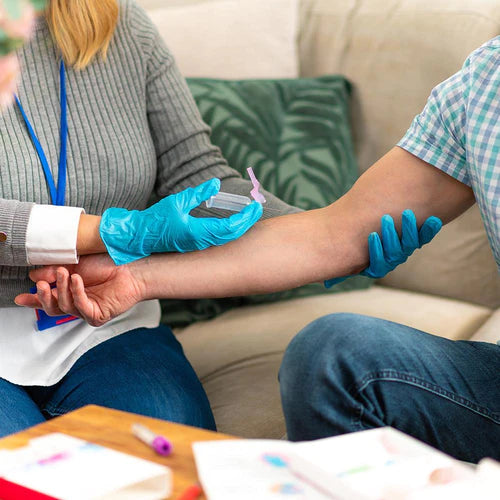
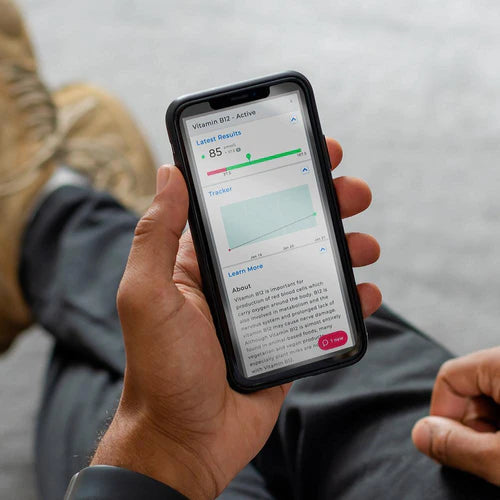
- Blood Test evaluates blood components
- provides information about overall health and immune system
Why People Choose Us

Quick & Easy
No appointment or long waiting times
Discreet Packaging
Plain packaging with no medical stamps or marks

Confidential Service
Your information stays with us and private payment

UK Medication
Dispensed by registered UK pharmacists
Red Blood Cells (7 Biomarkers)
The most prevalent form of blood cell, the red blood cell, is responsible for transporting oxygen to your tissues through your circulatory system.
Your bone marrow continuously produces red blood cells to replace those that are lost as a result of bleeding or cell ageing. Your red cell count should remain consistent, but some health issues can result in abnormally few or excessively numerous red cells, abnormally fast cell death, or abnormally shaped red cells.
The amount of oxygen given to your tissues is affected if you are not creating enough red blood cells, which causes anaemia and its accompanying symptoms of weariness and pale skin.
Headaches, blurred vision, and an enlarged spleen can all be symptoms of excessive red blood cell production.
Haematocrit
The haematocrit (HCT) scale measures how much space (volume) red blood cells occupy inside the blood.
Haemoglobin
Red blood cells contain the protein haemoglobin, which is responsible for the red colour of the blood and for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
This test gauges the blood's capacity to transport oxygen throughout the body by counting the amount of haemoglobin present.
Because they need to make sure that their muscles are getting enough oxygen, athletes and sports persons typically have higher oxygen demands than the normal person.
In endurance and strength athletes, it is typical to detect haemoglobin levels at the higher end of the normal range.
MCH
The average quantity of haemoglobin found in one of your red blood cells is measured by MCH (mean corpuscular haemoglobin).
MCHC
The average amount of haemoglobin in your red blood cells is called the MCHC (mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration).
Red blood cells use the chemical haemoglobin to carry oxygen throughout the body.
MCV
Your red blood cells' average size can be determined by your MCV (mean corpuscular volume).
This is crucial to evaluate because it can show how much oxygen your cells are probably transferring throughout the body.
RDW
The red blood cell distribution width (RDW) reveals whether the sizes and shapes of your red blood cells are uniform across the board or vary.
Your red blood cells may grow in atypical sizes due to several blood disorders because, in general, cells are pretty uniform in size and shape.
The size difference between the largest and the smallest red blood cell is determined by this test.
Red Cell Count
Analyzing the quantity of red blood cells in the blood is known as red blood cell (RBC) counting.
Oxygen is transported by red blood cells from the lungs to the rest of the body, where it can be used as a source of energy for activities like breathing and moving about. Additionally, they transport the carbon dioxide that cells make back to the lungs for exhalation.
Clotting Status (2 Biomarkers)
Your bone marrow produces your clotting cells (platelets), which are crucial for regulating bleeding.
Thrombocytopenia is a condition that occurs when too few or too quickly damaged platelets are created. Immune problems, certain medications, liver illness, or continuous bleeding are all potential causes of this.
Thrombocytosis, often known as a high platelet count, can result from a number of illnesses, including problems with the bone marrow, infection, and inflammation.
MPV
Mean Platelet Volume, or MPV, is a measurement of your platelets' typical size.
Blood cells that have been broken up into pieces are called platelets, and they help clots form. The creation of platelets in your bone marrow is indicated by MPV.
Platelet Count
The smallest form of blood cell, called platelets or clotting cells, are crucial for blood coagulation.
The platelets enlarge, cluster, and eventually form a sticky plug (a clot) that aids in stopping bleeding when it occurs.
White Blood Cells (6 Biomarkers)
The foundation of your body's immunological or defence system is made up of white blood cells. They combat illnesses and shield your body from external substances like dangerous bacteria and germs.
White blood cells are created from bone marrow stem cells and have a short lifespan of a few days. The body is protected by five main types of white blood cells, each of which has a unique function.
Your immune system and recent infections can both be diagnosed using the numbers of each of these categories of white blood cells.
White Cell Count
The White Blood Cell (WBC) Count calculates how many white blood cells are present in the blood. White blood cells are essential to the immune system of your body.
They combat illnesses and defend your body from invaders like dangerous bacteria and germs. To shield you from repeated infections with the same germ, they also develop a large number of antibodies and memory cells.
Basophils
White blood cells called basophils guard your body against bacteria and parasites like ticks. They additionally contribute to allergic responses.
Eosinophils
White blood cells called eosinophils are in charge of eliminating parasite infections and controlling inflammation to identify an infected spot. They also have an impact on asthma and allergies.
Lymphocytes
White blood cells called lymphocytes defend the body against viral and bacterial illnesses.
They are a subgroup of white blood cells that play a role in the body's more focused response to infections, which is able to recognise and classify various foreign organisms that enter the body. They create antibodies and memory cells to aid in preventing further infections from the same germ in addition to combating infection.
T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells are examples of lymphocytes.
Monocytes
White blood cells called monocytes engulf and eliminate pathogens as well as dead or damaged cells from our blood.
These cells' activity contribute to the heat and swell of inflammation.
Neutrophils
White blood cells known as neutrophils are in charge of assisting your body in the fight against illness. If your neutrophil count is low, you may be more susceptible to disease and infection.
Easy Steps for your Medicine

Complete a consultation.
With complete privacy and confidentiality your form is checked by a pharmacist independent prescriber.
Choose your treatment.
From the list approved by the prescriber, choose your preferred treatment and then wait for it to be dispensed by UK Meds online pharmacy.
Receive your delivery
With next day delivery options available, you can have your treatment sent out to you discreetly within hours.Our Happy Customers
Rated Us for our Service Excellence
 Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists
Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists

 How it works
How it works Help
Help Account
Account
 Basket
Basket