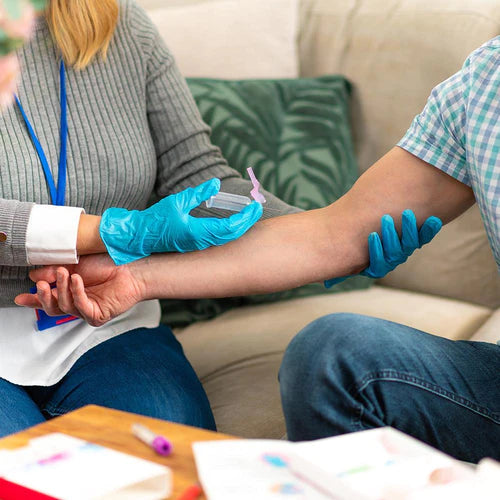
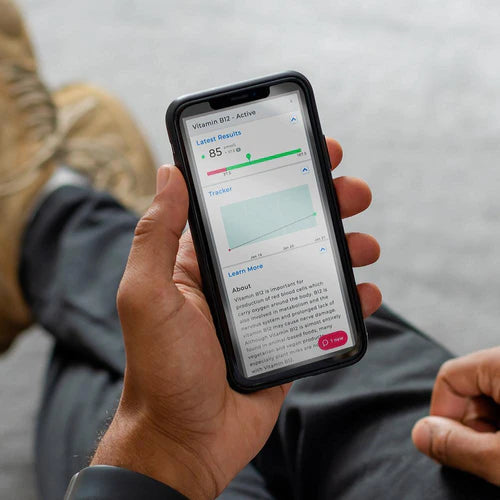
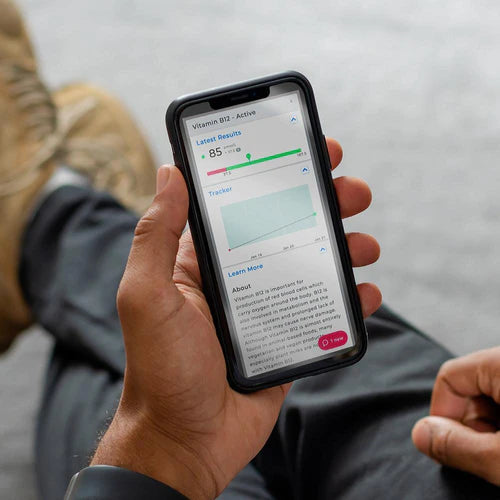
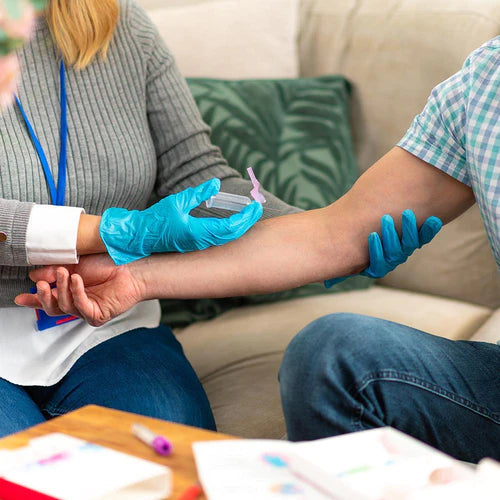
About Description
- measure the amount of apolipoprotein A1 and apolipoprotein B in the blood
Why People Choose Us

Quick & Easy
No appointment or long waiting times
Discreet Packaging
Plain packaging with no medical stamps or marks

Confidential Service
Your information stays with us and private payment

UK Medication
Dispensed by registered UK pharmacists
A fatty molecule called cholesterol is present in the blood and is crucial for the proper functioning of the body's cells.
But having too much cholesterol in your blood can seriously harm your health since it makes you more likely to experience a heart attack or stroke.
Numerous variables increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, and we continue to learn more about the intricate biochemical mechanisms that trigger a heart attack.
However, even then, it is not so straightforward because there are various forms of cholesterol, some of which are more dangerous than others. High levels of cholesterol have long been recognised to increase your risk.
In addition to coming from the food we eat, cholesterol is also produced in the liver. Diet, family history, obesity, and inactivity all have a negative effect on cholesterol levels.
In the organism, cholesterol is a necessary fat (lipid). Even though it has a terrible reputation, it performs a number of crucial tasks, such as creating cell membranes and a number of necessary hormones.
In addition to coming from the food we eat, cholesterol is also produced in the liver. The amount of both good (HDL) and bad (total) cholesterol in your blood is measured (LDL, VLDL and non HDL). When carbohydrate energy sources are scarce or for endurance activities, fats serve as the main energy source.
Medium-chain fatty acids in particular are used extensively. By examining the levels of the various forms of cholesterol, we can gain information into your health and cardiovascular risk.
Cholesterol distributes fatty acids throughout the body (i.e. the buildup of cholesterol in blood vessels leading to blood vessel narrowing, heart attack and stroke). The liver controls the amount of cholesterol in the body; it produces and eliminates it, and it also produces different lipoproteins that carry cholesterol throughout the body. It is these that the cholesterol test measures.
Low density lipoprotein, often known as LDL cholesterol, is a lipid and protein molecule that carries triglycerides, cholesterol, and other fats to various bodily regions. When fatty deposits build up inside artery walls due to an excess of LDL cholesterol, sometimes known as "bad cholesterol," this could result in atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Through food and exercise, your cholesterol levels can be dramatically reduced. Likewise, if you can raise your levels, you may be able to avoid developing significant, potentially fatal illnesses in the future.
Results for HDL and LDL (and non-HDL) can be used as benchmarks and improvement targets. Regular exercise, especially cardio and weight training, will help lower LDL and raise HDL. Cholesterol levels will also be optimised by a Mediterranean diet that is heavy in vegetables and oily fish and low in meat and dairy.
All of the cholesterol molecules that are not HDL (or "good" cholesterol") are referred to as non-HDL cholesterol. Therefore, it includes all of the potentially dangerous and non-protective cholesterol in your blood. As a result, it is thought to be a more accurate indicator of cardiovascular risk than LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol.
Less than 4 mmol/L of non-HDL cholesterol is advised. Through food and exercise, your cholesterol levels can be dramatically reduced.
Likewise, if you can raise your levels, you may be able to avoid developing significant, potentially fatal illnesses in the future. Results for HDL and LDL (and non-HDL) can be used as benchmarks and improvement targets.
Regular exercise, especially cardio and weight training, will help lower LDL and raise HDL. Cholesterol levels will also be optimised by a Mediterranean diet that is heavy in vegetables and oily fish and low in meat and dairy.
High Density Lipoprotein, often known as HDL cholesterol, is a molecule that transfers cholesterol from the bloodstream to the liver, where it is broken down and expelled from the body as bile.
The term "good cholesterol" refers to HDL cholesterol. Through food and exercise, your cholesterol levels can be dramatically reduced. Likewise, if you can raise your levels, you may be able to avoid developing significant, potentially fatal illnesses in the future.
Results for HDL and LDL (and non-HDL) can be used as benchmarks and improvement targets. Regular exercise, especially cardio and weight training, will help lower LDL and raise HDL. Cholesterol levels will also be optimised by a Mediterranean diet that is heavy in vegetables and oily fish and low in meat and dairy.
By dividing your total cholesterol value by your HDL cholesterol level, you can get your cholesterol/HDL ratio. It serves as a gauge of cardiovascular risk since it provides useful information about the percentage of "good" cholesterol in your total cholesterol (i.e. high-density lipoprotein, HDL).
The cholesterol/HDL ratio is used by heart disease risk calculators (like QRisk) to estimate your risk of suffering a heart attack.
The apoB/apoA ratio (apo-ratio) divides the amount of harmful Apolipoprotein B in the blood by the amount of beneficial Apolipoprotein A-I.
Results higher than this reflect an increase in the likelihood of having a heart attack or stroke in the future. A low value (usually below 1) is considered ideal.
Easy Steps for your Medicine

Complete a consultation.
With complete privacy and confidentiality your form is checked by a pharmacist independent prescriber.
Choose your treatment.
From the list approved by the prescriber, choose your preferred treatment and then wait for it to be dispensed by UK Meds online pharmacy.
Receive your delivery
With next day delivery options available, you can have your treatment sent out to you discreetly within hours.Our Happy Customers
Rated Us for our Service Excellence
 Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists
Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists

 How it works
How it works Help
Help Account
Account
 Basket
Basket