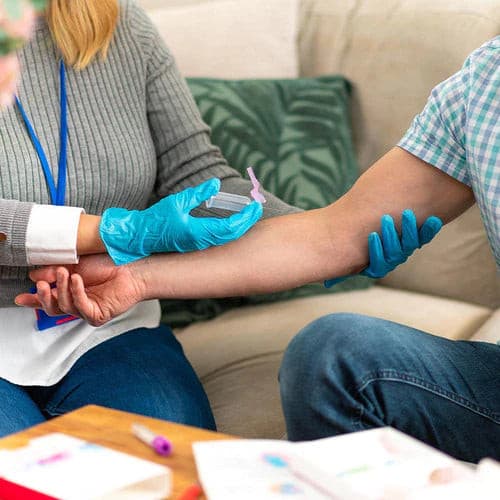
About Description
- test to check for energy and long-term health
- best Women's Ultimate Blood test
- Helps you to select the right treatment
Why People Choose Us

Quick & Easy
No appointment or long waiting times
Discreet Packaging
Plain packaging with no medical stamps or marks

Confidential Service
Your information stays with us and private payment

UK Medication
Dispensed by registered UK pharmacists
Thyroid Hormones (2 Biomarkers)
A gland at the front of your neck called the thyroid makes hormones that aid in regulating your metabolism.
Your thyroid may generate too little or too many thyroid hormones, and either situation can cause crippling symptoms. Lethargy, weight gain, dry skin, and hair are typical symptoms of an underactive thyroid, while nervousness and anxiety are typical signs of an overactive thyroid, as well as weight loss.
Once detected, thyroid disorders can be treated, but even then, it's crucial to keep an eye on your thyroid hormone levels to make sure they stay at their ideal levels.
TSH
The thyroid is a gland located near the base of the neck that regulates several metabolic processes, including substrate turnover, heart function, muscle physiology, and energy expenditure.
Thyroid dysfunction can cause either overproduction of hormones (overactive) or underproduction of hormones (underactive), both of which can lower athletic performance. The pituitary gland produces Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to create the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
As part of a neuroendocrine cascade, thyroid hormone synthesis occurs. Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) is released first in the hypothalamus, where it causes the pituitary to release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
To release the hormones T3 and T4, this attaches to thyroid gland cells (thyroxine). Additionally, peripheral tissues convert T4 into T3, the thyroid hormone with greater activity.These hormones are essentially what regulate your body's metabolism.
Negative feedback loops typically maintain a tight balance between all of these levels. Thyroid hormone over- or under-secretion can be a sign of abnormal thyroid function. These disorders frequently have an autoimmune component, which can frequently be detected by looking at your thyroid antibodies in more sophisticated thyroid tests.
Free Thyroxine
One of the two hormones that the thyroid gland produces is thyroxine (T4). It accelerates the rate at which your metabolism functions.
The majority of T4 in the blood is bound to carrier proteins, but this test solely measures free, or unbound, T4, which is active in the body.
Vitamins (2 Biomarker)
Your body requires vitamins as necessary nutrients to function properly. They must come from the food you consume because you cannot manufacture them yourself. There are two categories of vitamins: fat-soluble and water-soluble. Oily foods, whether animal- or plant-based, contain fat-soluble vitamins like vitamins A, D, E, and K.
You don't need to eat them every day because your body stores them in fatty tissue and the liver.You must consume meals containing these nutrients more regularly because the majority of water-based vitamins, such as vitamin C, are not stored in the body.
A balanced diet should provide you with all the vitamins you require. But occasionally, dietary decisions or medical issues might make us vitamin deficient.
Vitamin D
Together with calcium, vitamin D is essential for bone maintenance. It is crucial for both protein synthesis and muscle function.
Other non-musculoskeletal advantages, such as immunological regulation, defence against chronic diseases, and improved sports performance, have also been emphasised by more recent study.
Maintaining adequate amounts of vitamin D is crucial for athletes. When your skin is exposed to sunshine, it can produce vitamin D.
This is challenging in the UK, especially during the winter. Even if they exercise outside, people in the UK frequently have low vitamin D levels.
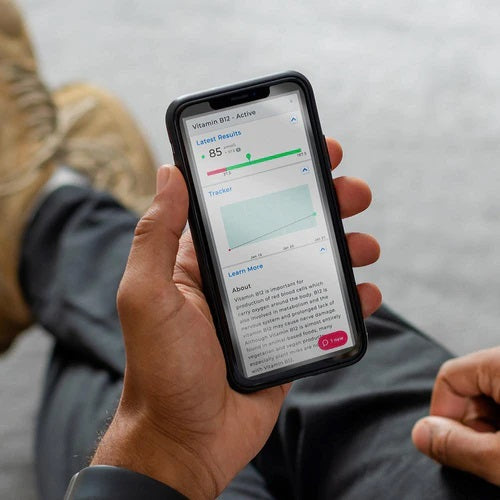
Vitamin B12- Active
The generation of red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body, depends on vitamin B12.
Additionally essential for metabolism and the nervous system, vitamin B12 deficiency can harm nerves over time.
Although plant milks are increasingly frequently enriched with vitamin B12, vitamin B12 is still nearly exclusively found in meals derived from animals.
Iron Status (1 Biomarker)
Ferritin
A complex globular protein called ferritin is used to store iron in an inactive form. The ferritin releases its iron for usage as your iron reserves get depleted.
You will run out of iron if your ferritin levels drop, and your ability to make red blood cells in your bone marrow will also suffer.
Thus, ferritin provides a reliable indication of your iron reserves. Ferritin can rise at times of infection, inflammation, or trauma because it is an acute phase protein as well.
Liver Health (4 Biomarkers)
One of your body's most vital organs, the liver performs a variety of tasks including converting food into energy, eliminating waste and toxins, and producing and regulating some hormones.
Through overeating, drinking alcohol, and contracting viral hepatitis, your liver can become inflamed and gradually harmed. Although your liver has extraordinary regeneration capabilities, liver disease is irreversible once inflammation has resulted in scarring (cirrhosis).
Blood tests evaluate the levels of several enzymes, and if they are elevated, it may be a sign that your liver is inflamed.
ALT
The liver produces the enzyme alanine transferase (ALT), which can suggest liver damage brought on by medications, alcohol, or viruses (hepatitis).
GGT
The liver enzyme gamma GT, sometimes referred to as gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), is increased in conditions affecting the liver and bile ducts.
To differentiate between liver and bone diseases, it is utilised in conjunction with ALP. As it is elevated in 75% of heavy drinkers, gamma GT is also used to diagnose alcohol consumption.
ALP
An enzyme called alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is mostly present in the liver and bones. Its measurement can reveal whether a person has any active liver, gallbladder, or bone conditions.
Bilirubin
Haemoglobin from red blood cells breaks down, producing bilirubin as a byproduct. Through the liver, the gallbladder stores and concentrates it before secreting it into the intestine.
Your body eliminates it through faeces and urine. Due to red blood cells disintegrating beneath the skin, bilirubin is what gives bruises their occasionally yellow colour.
Cholesterol Status (6 Biomarkers)
A fatty molecule called cholesterol is present in the blood and is crucial for the proper functioning of the body's cells.
But having too much cholesterol in your blood can seriously harm your health since it makes you more likely to experience a heart attack or stroke.
Numerous variables increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, and we continue to learn more about the intricate biochemical mechanisms that trigger a heart attack.
However, even then, it is not so straightforward because there are various forms of cholesterol, some of which are more dangerous than others. High levels of cholesterol have long been recognised to increase your risk.
In addition to coming from the food we eat, cholesterol is also produced in the liver. Diet, family history, obesity, and inactivity all have a negative effect on cholesterol levels.
Total Cholesterol
In the organism, cholesterol is a necessary fat (lipid). Even though it has a terrible reputation, it performs a number of crucial tasks, such as creating cell membranes and a number of necessary hormones. In addition to coming from the food we eat, cholesterol is also produced in the liver.
The amount of both good (HDL) and bad (total) cholesterol in your blood is measured (LDL, VLDL and non HDL).When carbohydrate energy sources are scarce or for endurance activities, fats serve as the main energy source.
Medium-chain fatty acids in particular are used extensively. By examining the levels of the various forms of cholesterol, we can gain information into your health and cardiovascular risk.
Cholesterol distributes fatty acids throughout the body (i.e. the buildup of cholesterol in blood vessels leading to blood vessel narrowing, heart attack and stroke).The liver controls the amount of cholesterol in the body; it produces and eliminates it, and it also produces different lipoproteins that carry cholesterol throughout the body. It is these that the cholesterol test measures.
LDL Cholesterol
Low density lipoprotein, often known as LDL cholesterol, is a lipid and protein molecule that carries triglycerides, cholesterol, and other fats to various bodily regions.
When fatty deposits build up inside artery walls due to an excess of LDL cholesterol, sometimes known as "bad cholesterol," this could result in atherosclerosis and heart disease.Through food and exercise,
your cholesterol levels can be dramatically reduced. Likewise, if you can raise your levels, you may be able to avoid developing significant, potentially fatal illnesses in the future. Results for HDL and LDL (and non-HDL) can be used as benchmarks and improvement targets.
Regular exercise, especially cardio and weight training, will help lower LDL and raise HDL. Cholesterol levels will also be optimised by a Mediterranean diet that is heavy in vegetables and oily fish and low in meat and dairy.
Non-HDL Cholesterol
All of the cholesterol molecules that are not HDL (or "good" cholesterol") are referred to as non-HDL cholesterol.
Therefore, it includes all of the potentially dangerous and non-protective cholesterol in your blood. As a result, it is thought to be a more accurate indicator of cardiovascular risk than LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol. Less than 4 mmol/L of non-HDL cholesterol is advised.
Through food and exercise, your cholesterol levels can be dramatically reduced. Likewise, if you can raise your levels, you may be able to avoid developing significant, potentially fatal illnesses in the future.Results for HDL and LDL (and non-HDL) can be used as benchmarks and improvement targets. Regular exercise, especially cardio and weight training, will help lower LDL and raise HDL.
Cholesterol levels will also be optimised by a Mediterranean diet that is heavy in vegetables and oily fish and low in meat and dairy.
HDL Cholesterol
High Density Lipoprotein, often known as HDL cholesterol, is a molecule that transfers cholesterol from the bloodstream to the liver, where it is broken down and expelled from the body as bile.
The term "good cholesterol" refers to HDL cholesterol. Through food and exercise, your cholesterol levels can be dramatically reduced. Likewise, if you can raise your levels, you may be able to avoid developing significant, potentially fatal illnesses in the future.Results for HDL and LDL (and non-HDL) can be used as benchmarks and improvement targets.
Regular exercise, especially cardio and weight training, will help lower LDL and raise HDL. Cholesterol levels will also be optimised by a Mediterranean diet that is heavy in vegetables and oily fish and low in meat and dairy.
Total Cholesterol/HDL
By dividing your total cholesterol value by your HDL cholesterol level, you can get your cholesterol/HDL ratio.
It serves as a gauge of cardiovascular risk since it provides useful information about the percentage of "good" cholesterol in your total cholesterol (i.e. high-density lipoprotein, HDL).
The cholesterol/HDL ratio is used by heart disease risk calculators (like QRisk) to estimate your risk of suffering a heart attack.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are a type of lipid that move through the bloodstream. They are transported in the bloodstream by chylomicrons and VLDLs, two types of lipoproteins (very low density lipoproteins).
Following a meal, extra calories are converted by your body into triglycerides, which are subsequently carried to cells where they are stored as fat. Triglycerides are then released by your body when it needs energy.
Kidney Health (2 Biomarkers)
Waste materials and extra fluid are taken out of your blood by your kidneys.
Examining the levels of waste products in the blood as well as the levels of electrolytes, which control fluid in the body, can be used to gauge how effectively they are performing their duties.
Early kidney disease signs are usually nonexistent, so it's crucial to keep an eye on kidney function, particularly if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a close relative who has the condition.
Creatinine
The regular breakdown of muscles produces the chemical waste molecule creatinine. Therefore, athletes are capable of higher levels than the normal person.
Since creatinine is excreted by the kidneys, it can be used to diagnose renal disease and is a reliable indicator of kidney function.
EGFR
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), which calculates how much blood is filtered through the kidneys, measures how well the kidneys are functioning. The kidneys' glomeruli are microscopic filters that remove waste materials.
Kidney function may be hampered if these filters do not operate adequately. Your age, gender, ethnicity, and serum creatinine levels are used to compute your estimated glomerular filtration rate, or eGFR.
Easy Steps for your Medicine

Complete a consultation.
With complete privacy and confidentiality your form is checked by a pharmacist independent prescriber.
Choose your treatment.
From the list approved by the prescriber, choose your preferred treatment and then wait for it to be dispensed by UK Meds online pharmacy.
Receive your delivery
With next day delivery options available, you can have your treatment sent out to you discreetly within hours.Our Happy Customers
Rated Us for our Service Excellence
 Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists
Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists

 How it works
How it works Help
Help Account
Account
 Basket
Basket