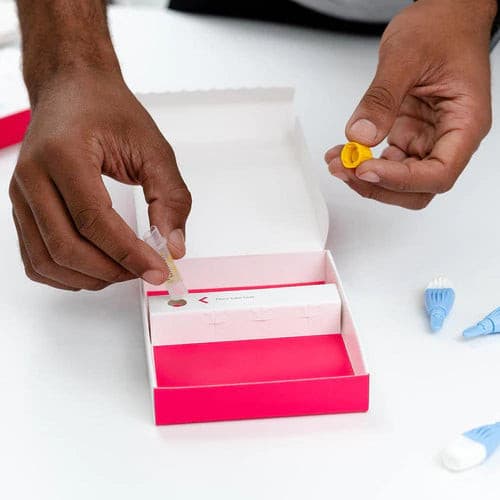
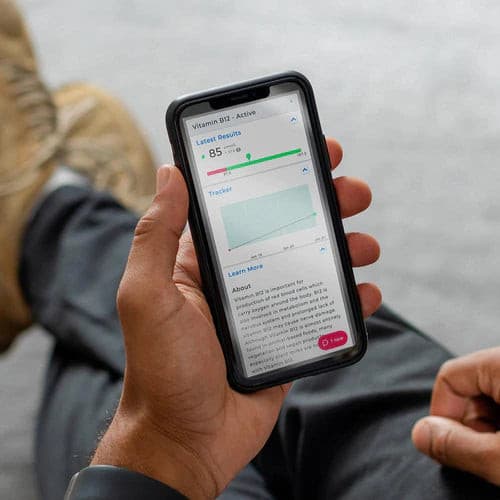
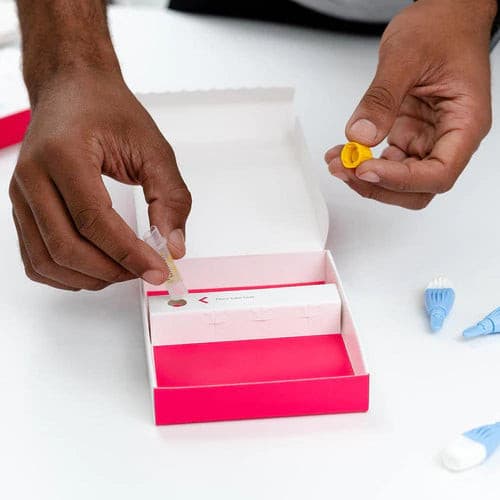
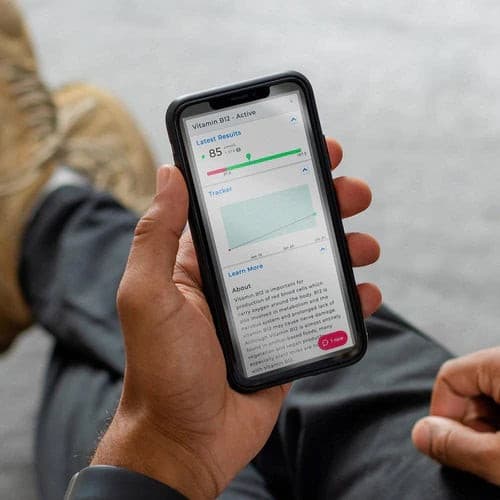
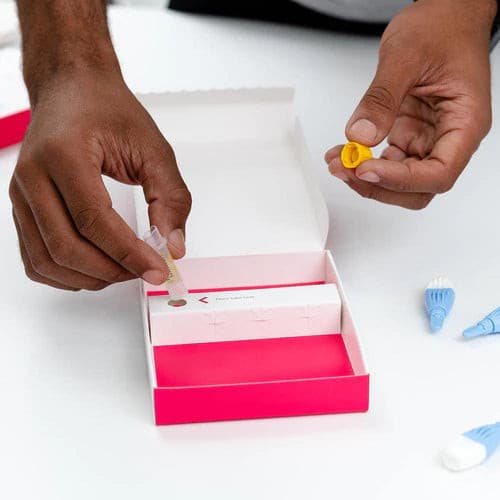
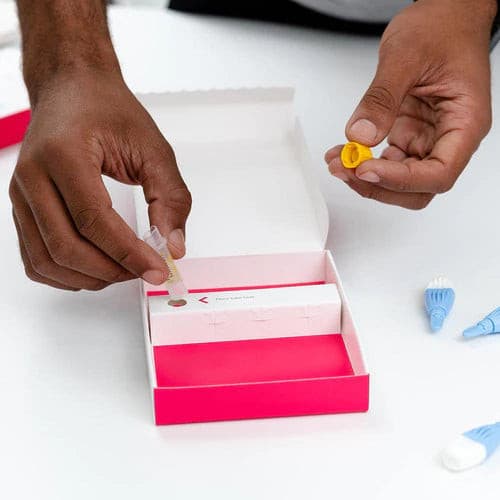
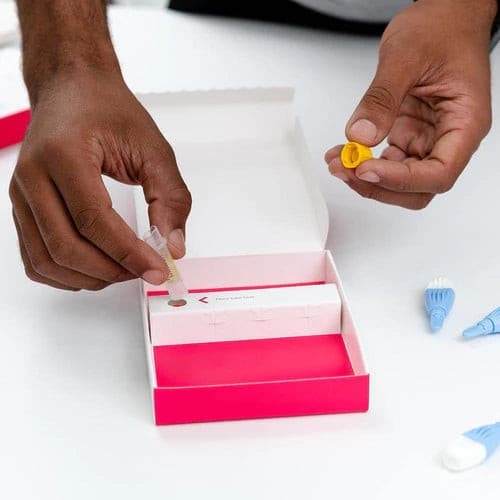
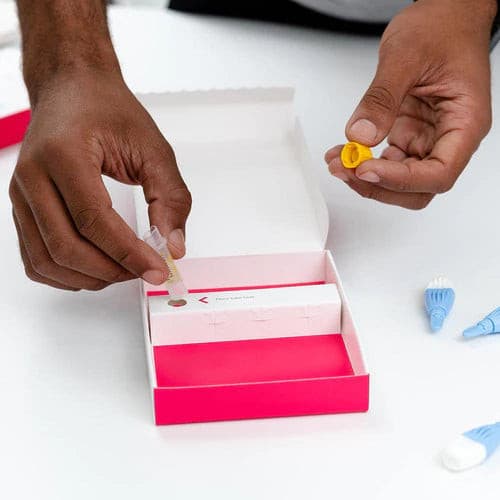
About Description
- measures 5 key hormones to assess menopausal status
- menopause blood test is ideal for women
Why People Choose Us

Quick & Easy
No appointment or long waiting times
Discreet Packaging
Plain packaging with no medical stamps or marks

Confidential Service
Your information stays with us and private payment

UK Medication
Dispensed by registered UK pharmacists
Every bodily function, including development, metabolism, reproduction, and sleep cycles, is controlled by hormones.
Your mood and energy levels, as well as your fertility and libido, can all be negatively impacted by even a slight hormonal imbalance.
Chemical messengers known as hormones are produced in your glands and delivered into your bloodstream. Your body receives instructions from them on how to control your appetite, growth, mood, and reproduction.
In general, they maintain the body's equilibrium and functionality. Hormone imbalances are frequently treated with hormone replacement therapy or by altering one's lifestyle. Throughout the day and for women during the menstrual cycle, hormone levels change
The pituitary gland produces the hormone follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which is crucial for both men and women in the development of sperm and eggs.
FSH increases the growth of follicles within the ovaries in the first half of the menstrual cycle in women.
Oestradiol is a female steroid hormone that is made primarily in women's ovaries and only little in men's testicles.
The female reproductive system, breast tissue growth, and bone density are all influenced by this, the strongest of the three oestrogens. Oestradiol levels in premenopausal women fluctuate during the monthly cycle, reaching their highest point at ovulation.
Oestradiol levels in women decrease with ageing, peaking at menopause when the ovaries stop releasing eggs. Low oestradiol can induce several symptoms associated with the menopause, including hot flushes, nocturnal sweats and mood swings. Osteoporosis can also result from low oestradiol.
A gland at the front of your neck called the thyroid makes hormones that aid in regulating your metabolism.
Your thyroid may generate too little or too many thyroid hormones, and either situation can cause crippling symptoms. Lethargy, weight gain, dry skin, and hair are typical symptoms of an underactive thyroid, while nervousness and anxiety are typical signs of an overactive thyroid, as well as weight loss.
Once detected, thyroid disorders can be treated, but even then, it's crucial to keep an eye on your thyroid hormone levels to make sure they stay at their ideal levels.
The thyroid is a gland located near the base of the neck that regulates several metabolic processes, including substrate turnover, heart function, muscle physiology, and energy expenditure.
Thyroid dysfunction can cause either overproduction of hormones (overactive) or underproduction of hormones (underactive), both of which can lower athletic performance. The pituitary gland produces Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to create the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
As part of a neuroendocrine cascade, thyroid hormone synthesis occurs. Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) is released first in the hypothalamus, where it causes the pituitary to release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
To release the hormones T3 and T4, this attaches to thyroid gland cells (thyroxine). Additionally, peripheral tissues convert T4 into T3, the thyroid hormone with greater activity.These hormones are essentially what regulate your body's metabolism.
Negative feedback loops typically maintain a tight balance between all of these levels. Thyroid hormone over- or under-secretion can be a sign of abnormal thyroid function. These disorders frequently have an autoimmune component, which can frequently be detected by looking at your thyroid antibodies in more sophisticated thyroid tests.
One of the two hormones that the thyroid gland produces is thyroxine (T4). It accelerates the rate at which your metabolism functions.
The majority of T4 in the blood is bound to carrier proteins, but this test solely measures free, or unbound, T4, which is active in the body.
Easy Steps for your Medicine

Complete a consultation.
With complete privacy and confidentiality your form is checked by a pharmacist independent prescriber.
Choose your treatment.
From the list approved by the prescriber, choose your preferred treatment and then wait for it to be dispensed by UK Meds online pharmacy.
Receive your delivery
With next day delivery options available, you can have your treatment sent out to you discreetly within hours.Our Happy Customers
Rated Us for our Service Excellence
 Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists
Dispensed by Regulated UK Pharmacists

 How it works
How it works Help
Help Account
Account
 Basket
Basket